Most articles on crypto exchange development stop at surface-level explanations.
This one doesn’t.
If you’re reading this, you already know what a crypto exchange is. The real questions now are:
Why do most exchanges fail after launch?
Where do costs silently explode?
Why liquidity integrations break under real traffic?
Why “white label” exchanges often hit a scalability wall?
What actually differentiates a serious crypto exchange development company from a code vendor?
This guide addresses those exact gaps-based on real-world exchange builds for India, the United States, and global markets.
Forget UI.
Forget token listings.
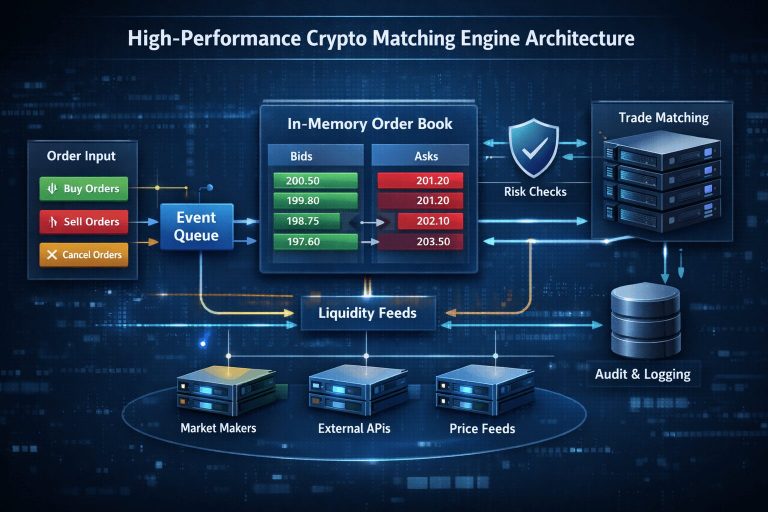
Your exchange lives or dies by matching engine performance under stress.
Deterministic order matching (price-time priority)
Sub-millisecond latency under burst traffic
Ability to process 10k–100k TPS spikes
Graceful degradation during volatility events
Most off-the-shelf engines fail when:
Market makers pull liquidity
Order cancellations spike 10x
Bots exploit queue latency
Advanced crypto exchange software development uses:
In-memory order books
Event-driven architectures
Write-ahead logging for recovery
Separate risk engines per trading pair
This is where serious engineering budgets go – and where cheap builds collapse.
Liquidity is often misunderstood as a one-time integration.
It isn’t.
Fake depth from shared LP pools
Arbitrage draining INR/USDT pairs
Latency mismatch between LPs
Slippage during volatile markets
Advanced exchanges:
Combine external LPs + internal market making
Use spread control logic
Implement volatility circuit breakers
Isolate LP failure from retail order flow
Any crypto exchange development company that promises “deep liquidity in 48 hours” without discussing risk offsets and pair-specific behavior is overselling.
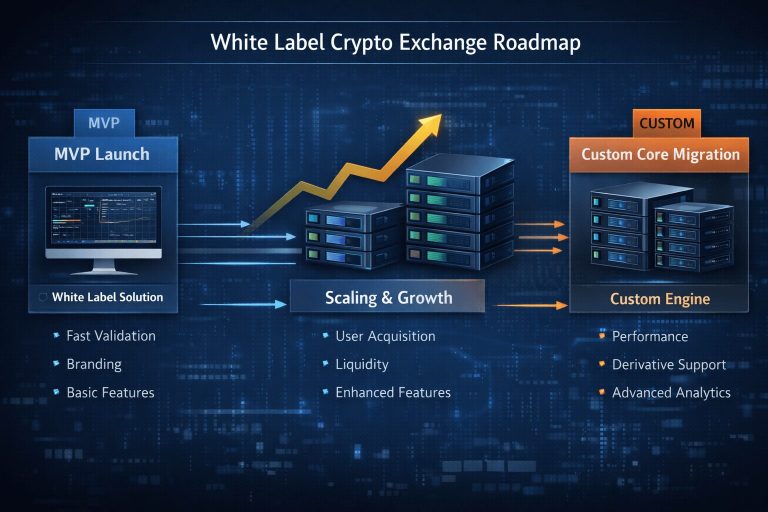
White label is not bad.
Blind white label usage is.
You launch fast to test market demand
You accept architectural constraints
You plan a Phase-2 custom engine
Daily active traders exceed ~8–12k
You introduce derivatives or P2P
You need regulatory-specific flows (US vs India)
You require exchange-level analytics
Smart founders use white label as a launchpad-not a permanent foundation.
Most cost estimates online are misleading because they ignore operational complexity.
Security audits (ongoing, not one-time)
Compliance workflows (manual reviews scale badly)
Liquidity risk buffers
Cloud cost during volatility spikes
Support + fraud response teams
| Component | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Matching Engine (Custom) | $25k–50k |
| Wallet Infrastructure | $10k–20k |
| White Label Core | $35k–70k |
| Mobile Apps | $15k–30k |
| Security & Audits | $10k–25k |
| Liquidity Setup | $5k–20k |
A production-grade exchange is rarely under $60k–$120k when done correctly.
Compliance is not a checkbox—it’s system design.
KYC workflow branching
Suspicious activity monitoring
Audit logs that regulators can replay
Reference:
FinCEN MSB Requirements
INR rails integration
Transaction-level traceability
FIU reporting structure
Poor compliance design = manual ops = rising costs = stalled growth.
Mobile apps fail when:
Web sockets choke under market spikes
Order states desync
Wallet balances lag
Advanced apps:
Use real-time state reconciliation
Separate trading & wallet APIs
Implement offline-safe order states
Support biometric + hardware-backed security
This is the blueprint experienced founders follow:
Launch with controlled features
Limit pairs initially
Simulate extreme volatility pre-launch
Design for regulatory evolution
Migrate architecture before scaling hurts
Most exchanges don’t fail because of lack of demand.
They fail because the foundation can’t handle success.
Avoid teams that:
Promise “Binance clone in 30 days”
Can’t explain order matching logic
Don’t ask about liquidity strategy
Ignore compliance early
Work with a crypto exchange development company that:
Talks in trade-offs, not promises
Designs for scaling pain
Understands US + India market differences
Thinks like an exchange operator-not an agency
In 2026, building a crypto exchange is no longer a tech challenge-it’s a systems engineering and risk management problem.
The difference between exchanges that survive and those that disappear is not features.
It’s architecture, liquidity control, and execution discipline.
Enter your email → Get instant download.