The Web3 ecosystem faced a harsh reality in 2025: over $3.1 billion was drained from blockchain protocols in just the first six months—making it the worst year for crypto crime on record. Behind these staggering losses lie smart contract vulnerabilities that could have been prevented with proper security practices.
As blockchain technology becomes integral to finance, gaming, and enterprise solutions, securing Web3 ledgers through robust smart contract development isn’t just best practice—it’s mission-critical. Whether you’re building DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, or tokenization platforms, understanding smart contract security can mean the difference between success and catastrophic failure.
This comprehensive guide explores the critical security vulnerabilities threatening Web3 ledgers today and provides actionable best practices to protect your smart contracts from exploitation.
A Web3 ledger is a distributed, immutable database that records transactions across a blockchain network. Unlike traditional databases, Web3 ledgers operate without central authority, relying on cryptographic protocols and consensus mechanisms to maintain data integrity. Smart contracts—self-executing code deployed on these ledgers—automate transactions and enforce rules without intermediaries.
The decentralized nature of Web3 ledgers creates unique security challenges. Once deployed, smart contracts become immutable, meaning vulnerabilities cannot be easily patched. This permanence, combined with the financial value locked in smart contracts, makes them attractive targets for attackers. Security research from 2025 reveals that access control vulnerabilities alone caused $953.2 million in losses, highlighting the critical need for secure development practices.
According to the OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 (2025), here are the most critical vulnerabilities threatening Web3 ledgers:
Poorly implemented permissions and role-based access controls allow unauthorized users to execute privileged functions. Common issues include exposed admin functions, weak onlyOwner modifiers, and insufficient role-based access control (RBAC).
Prevention:
DeFi protocols heavily rely on oracles for price feeds. Attackers manipulate these data sources to create artificial price movements, draining liquidity pools through flash loans and arbitrage.
Real-world example: The BonqDAO hack exploited a price oracle vulnerability, allowing attackers to steal 100 million $BEUR stablecoins and 120 million $WALBT.
Prevention:
Flaws in business logic or calculation errors can be exploited for financial gain. These vulnerabilities often arise from edge cases, incorrect mathematical operations, or flawed reward distribution mechanisms.
Prevention:
Despite being known since The DAO hack in 2016, reentrancy remains a top exploit vector. This vulnerability occurs when external calls are made before updating contract state, allowing malicious contracts to repeatedly call back into the original function.
Vulnerable code example:
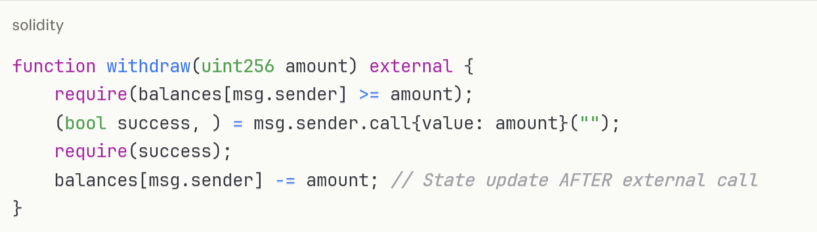
Secure implementation:
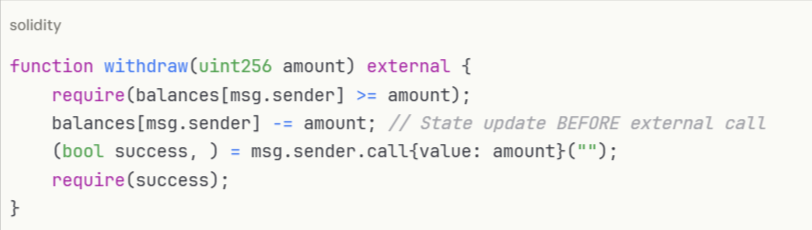
Prevention:
Flash loans enable attackers to borrow massive amounts without collateral, manipulate markets, and exploit protocol vulnerabilities within a single transaction.
Real-world example: Sonne Finance lost $20 million in May 2024 when attackers used flash loans to manipulate governance permissions.
Prevention:
When arithmetic operations exceed the maximum or minimum values of data types, unexpected behavior occurs, potentially allowing attackers to manipulate token balances or contract logic.
Prevention:
Insufficient validation of user inputs allows attackers to pass malicious data that triggers unintended behavior.
Prevention:
Failing to check return values from external calls can lead to silent failures and unexpected contract states.
Prevention:
Attackers exhaust contract resources (gas, CPU, storage) to make contracts unusable or manipulate outcomes.
Prevention:
Attackers monitor pending transactions and submit their own with higher gas fees to execute before the original transaction, profiting from price movements.
Prevention:
Professional audits identify vulnerabilities that automated tools miss. Security firm data shows that comprehensive audits have prevented billions in potential losses.
Audit process:
Reinventing security mechanisms increases vulnerability risks. Leverage battle-tested libraries that have undergone extensive auditing.
Recommended libraries:
Integrate security tools into your development pipeline to catch vulnerabilities early.
Top security tools for 2025:
Static Analysis:
Fuzzing:
Formal Verification:
AI-Powered:
Implement security at every stage of development:
Planning Phase:
Development Phase:
Testing Phase:
Pre-Deployment:
Post-Deployment:
Distribute control to prevent single points of failure:
Gas optimization can introduce vulnerabilities. Balance efficiency with security:
Clear documentation prevents misunderstandings and aids security reviews:
This fundamental pattern prevents reentrancy and ensures state consistency:
Instead of pushing payments to recipients, allow them to withdraw:
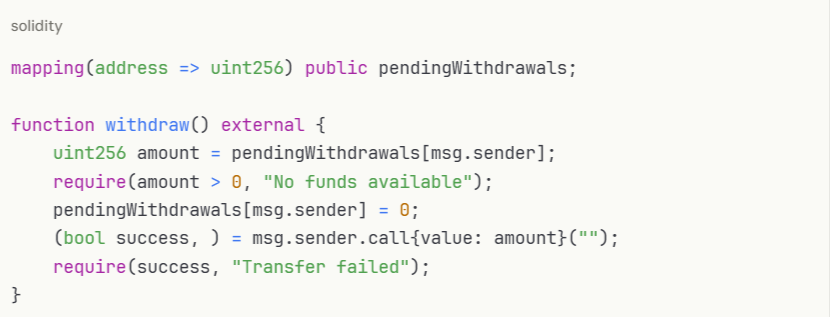
Implement emergency pause functionality:

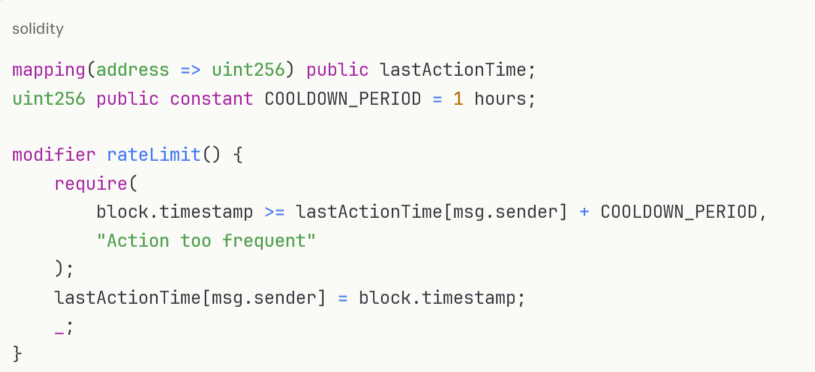
Prevent abuse through transaction rate limits:
Despite best efforts, incidents may occur. Prepare accordingly:
Vulnerability: Reentrancy attack Loss: $60 million (3.6 million ETH) Lesson: Always update state before external calls; implement reentrancy guards
Vulnerability: Flash loan attack on governance Loss: $20 million Lesson: Implement anti-flash-loan mechanisms in governance systems
Vulnerability: Price oracle manipulation Loss: 100 million $BEUR + 120 million $WALBT Lesson: Use decentralized oracles with multiple data sources
As Web3 matures, regulatory scrutiny increases:
AI-Powered Security: Machine learning models trained on thousands of audit reports now detect complex vulnerabilities. Tools like AuditBase demonstrate the potential of AI in smart contract security.
Formal Verification Adoption: Mathematical proofs of contract correctness are becoming standard for high-value protocols.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: ZK technology enables privacy while maintaining security verifiability.
Automated Incident Response: Smart contracts with built-in detection and response capabilities.
Security is an ongoing process:
Web3 ledger security begins with secure smart contract development. The $3.1 billion lost in 2025 demonstrates that security cannot be an afterthought—it must be embedded in every development phase.
By implementing the best practices outlined in this guide, you can significantly reduce vulnerability risks:
✅ Conduct comprehensive security audits ✅ Use established security libraries and patterns ✅ Integrate automated security tools in your pipeline ✅ Follow secure development lifecycles ✅ Implement defense-in-depth strategies ✅ Prepare incident response procedures ✅ Stay updated on emerging threats
Remember: In Web3, security isn’t just about protecting code—it’s about protecting user trust and the future of decentralized technology.
At Chainbull, we specialize in secure Web3 development and smart contract auditing. Our team of blockchain security experts has helped hundreds of projects launch safely across Ethereum, Solana, Binance Smart Chain, and other major networks.
Our Security Services:
Ready to build secure Web3 applications? Contact our experts today for a free security consultation.
Enter your email → Get instant download.